What is Money Laundering?
Money laundering is the process of disguising the illegal source of funds. It’s like taking paint-stained bills and running them through a complex financial washing machine. They emerge clean and seemingly legitimate, ready to re-enter the financial system without raising suspicion.
Money laundering is a serious threat that needs to be controlled for a number of reasons. Firstly, it allows criminals to keep the profits from their illegal activities, reinvesting that money back into crime. This cycle fuels drug trafficking, human smuggling, and other harmful operations. Additionally, laundered money can destabilize economies, distort markets and weaken institutions.
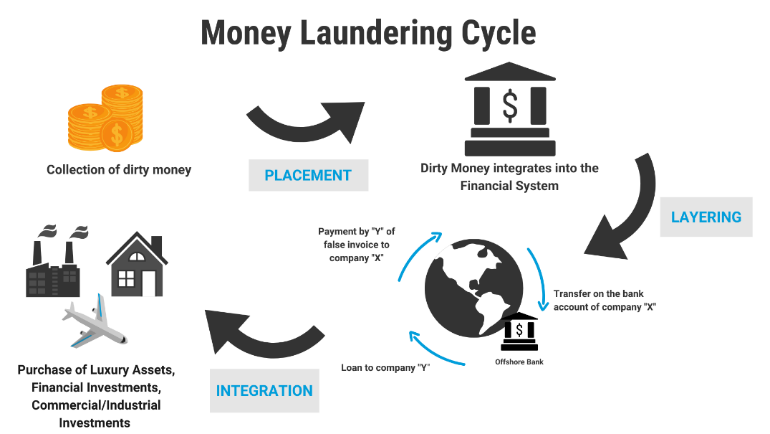
Source: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
In order to tackle this problem, Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 was introduced. The PMLA seeks to combat money laundering in India and has three main objectives:
- To prevent and control money laundering.
- To confiscate and seize the property obtained from the laundered money; and
- To deal with any other issue connected with money laundering in India.
In a move to strengthen India’s fight against money laundering, the government has expanded the law to include more parties who must report suspicious activity. They’ve also changed how financial transactions are tracked, giving authorities greater oversight. These adjustments aimed to make the system more efficient and aligned with international standards. The changes saw an increase in the number of cases being reported under PMLA.
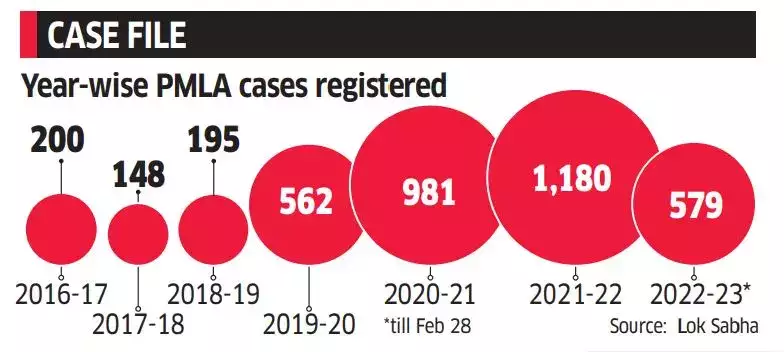
Source: Economic Times
Anti-money laundering isn’t just about safeguarding the financial system from criminals, It’s also a powerful tool in the fight against fraud. Since fraudsters often use money laundering tactics to disguise their ill-gotten gains, strong AML programs can help identify and stop them. These programs, which involve verifying customer information, monitoring transactions, and reporting suspicious activity, play a crucial role in protecting companies. By requiring financial institutions to verify the identity of their customers and report suspicious activity, anti-money laundering measures make it harder to support criminal activity. Developing a clear AML checklist ensures companies are prepared to tackle both money laundering and fraud effectively.
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) can however create several challenges for companies in India. Here’s a breakdown of the main difficulties:
- Compliance Burden: PMLA regulations require companies to implement robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. Maintaining these systems can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for smaller businesses.
- Stringent Penalties: Non-compliance with PMLA can lead to hefty financial penalties and even imprisonment for executives. Such penalties can be a significant burden for companies.
- Evolving Regulations: The PMLA and its interpretations are constantly evolving. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging for companies, requiring continuous training and updates to compliance procedures.
- Lack of Clarity: In some cases, the PMLA regulations may be unclear or open to interpretation. This ambiguity can make it difficult for companies to understand their exact obligations and increase the risk of unintentional non-compliance.
- Reputational Damage: Being associated with money laundering can severely damage a company’s reputation. Even if a company is ultimately cleared of wrongdoing, the investigative process itself can be damaging.
The PMLA presents a double-edged sword for companies in India. While it safeguards the financial system and combats criminal activity, compliance can be onerous. Companies must thus strike a balance between robust AML practices and streamlined operations. Fortunately, effective AML programs can also benefit businesses by mitigating fraud risk. By staying informed of legal developments and implementing AML programs efficiently, companies can navigate these challenges and emerge stronger.

